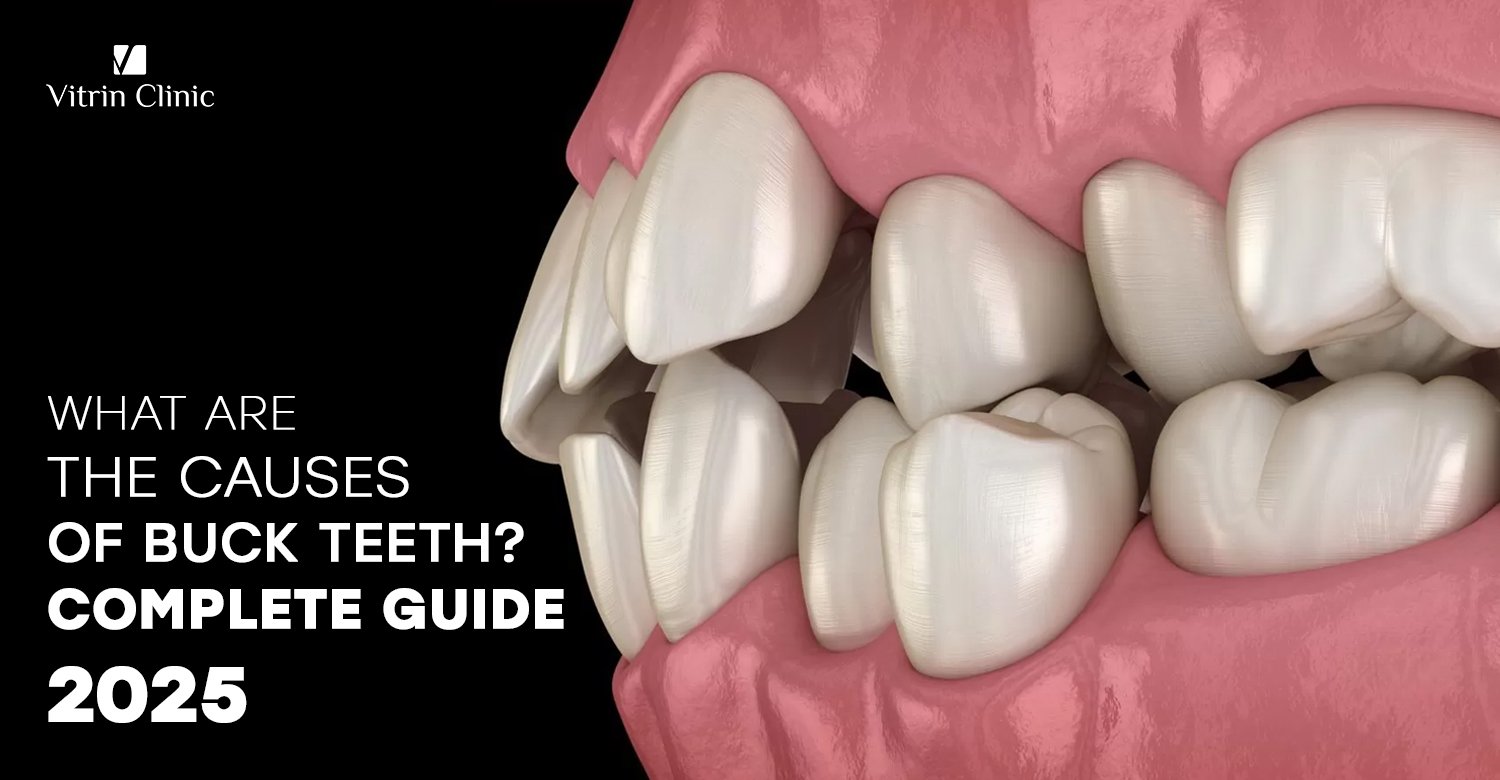
What Are the Primary Causes of Buck Teeth?
Buck teeth, medically known as dental protrusion or overjet, refer to a condition where the upper front teeth extend significantly beyond the lower teeth. This condition can arise from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
While habits like thumb-sucking or prolonged pacifier use can push the teeth outward during early development, genetics play a foundational role in predisposing individuals to buck teeth.
In many cases, the structure and alignment of the jaw and teeth are inherited, making it more likely for family members to share similar dental characteristics. Understanding these root causes is essential for effective treatment and prevention strategies.
What Genetic Factors Lead to Buck Teeth Development?
Genetics play a major role in the development of buck teeth. If one or both parents have an overbite or prominent upper jaw, there’s a high likelihood the trait could be passed on to their children. The size and shape of the jaw, the positioning of teeth, and even the growth pattern of facial bones are largely inherited.
These genetic components can lead to structural imbalances where the upper jaw grows faster or larger than the lower jaw, resulting in buck teeth. Although environmental influences can worsen the condition, genetics often set the stage for its development.
How Do Hereditary Traits Influence Tooth Positioning?
Hereditary traits, such as the size and spacing of teeth, can significantly affect how the teeth are positioned in the mouth. If a child inherits large teeth from one parent and a small jaw from the other, overcrowding or protrusion can occur.
Similarly, if the jawbone grows unevenly or disproportionately, it can result in misaligned teeth. These genetic patterns may not only cause buck teeth but also contribute to other malocclusions like underbites or crossbites. Dental alignment is often a visible expression of inherited craniofacial traits, which explains why orthodontic issues frequently run in families.
What Role Does Family History Play in Buck Teeth Formation?
Family history provides strong clues about whether an individual is predisposed to buck teeth. If multiple members of a family have prominent overbites or required orthodontic treatment for similar issues, it’s likely due to shared genetic traits. In some cases, these patterns span generations.
Orthodontists often review family dental history to assess a child’s risk and predict the need for early intervention. While not all inherited traits lead directly to buck teeth, a family history of dental misalignment increases the chances, especially when combined with environmental triggers like mouth breathing or prolonged pacifier use.
How Do Inherited Jaw Size Discrepancies Cause Protrusion?
One of the most common hereditary causes of buck teeth is a mismatch in jaw size. For example, if the upper jaw is significantly larger or grows more rapidly than the lower jaw, the upper front teeth can extend outward, creating a visible overjet.
Conversely, if the lower jaw is underdeveloped or receded, it can also make the upper teeth appear more prominent. These jaw discrepancies are often passed down through generations and can lead to significant bite issues. Orthodontic treatment usually involves correcting this imbalance through braces, retainers, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Which Genetic Conditions Are Most Associated with Buck Teeth?
Certain genetic conditions are strongly linked to dental protrusion. These conditions often affect the overall growth and structure of the face, jaws, and teeth. For example, cleft palate, Down syndrome, and Marfan syndrome can all influence tooth positioning and alignment.
These syndromes may involve delayed tooth eruption, malformed jawbones, or irregular dental arches, all of which contribute to the development of buck teeth. Recognizing the presence of these conditions early allows for coordinated care between orthodontists, pediatricians, and sometimes surgeons to address both functional and aesthetic concerns associated with buck teeth.
How Does Cleft Palate Contribute to Tooth Misalignment?
A cleft palate is a congenital condition where the roof of the mouth doesn’t fully close during fetal development. This can severely impact the alignment of teeth and the structure of the jaw. Children with cleft palates often experience misaligned teeth, including protruding front teeth due to insufficient bone support in the upper jaw.
The cleft can also affect the growth trajectory of the jaw, leading to imbalances that cause buck teeth. Early intervention, including surgery and orthodontic treatment, is crucial in managing this condition and minimizing long-term dental issues related to protrusion.
What Inherited Syndromes Cause Dental Protrusion?
Several inherited syndromes are known to cause buck teeth or similar dental protrusions. Marfan syndrome, a connective tissue disorder, often includes high-arched palates and overbites as part of its clinical presentation. Down syndrome can result in smaller jaws and larger tongues, leading to forward-angled teeth.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, another connective tissue disorder, may affect jaw stability and tooth positioning. These genetic syndromes disrupt normal craniofacial development, making it more likely for affected individuals to have buck teeth. Addressing dental protrusion in these cases often requires a comprehensive, multidisciplinary treatment plan.
How Do Chromosomal Abnormalities Affect Tooth Development?
Chromosomal abnormalities can influence the timing, size, and alignment of tooth development. For example, individuals with Down syndrome often have delayed tooth eruption and smaller jawbones, which contribute to crowding or protrusion of the front teeth.
These chromosomal differences affect the body’s blueprint for growth, leading to changes in bone density, jaw shape, and facial proportions. Such variations often result in misaligned teeth or overjet. Recognizing these abnormalities early can help orthodontists create customized treatment plans to manage buck teeth effectively while considering the patient’s overall health and developmental profile.
What Impact Do Growth Disorders Have on Dental Structure?
Growth disorders can significantly affect the development of the jaw and teeth, often leading to buck teeth. Conditions such as growth hormone deficiency or gigantism influence how bones grow, including those in the face and jaw.
If the upper jaw grows faster or more extensively than the lower jaw, the front teeth may protrude. On the other hand, underdevelopment of the lower jaw can also create a noticeable overjet. Children with growth disorders may require more frequent dental monitoring and early orthodontic assessment to correct or minimize misalignment as they grow.
How Do Childhood Habits Contribute to Buck Teeth Formation?
Childhood habits play a significant role in the development of buck teeth, especially during the formative years when the jaw and teeth are still growing. Behaviors such as thumb sucking, prolonged pacifier use, tongue thrusting, and certain lip habits can gradually push the front teeth forward, leading to a visible overjet.
These habits exert continuous pressure on the upper jaw and teeth, disrupting their natural alignment. If not addressed early, these patterns can lead to long-term orthodontic issues that require intervention. Understanding the impact of these habits helps parents take timely steps to prevent buck teeth in children.
What Role Does Thumb Sucking Play in Tooth Protrusion?
Thumb sucking is one of the most common childhood habits linked to buck teeth development. When a child sucks their thumb regularly, it places pressure on the roof of the mouth and the back of the upper front teeth. Over time, this pressure can cause the teeth to move forward and the upper jaw to narrow, creating a misaligned bite or overjet.
The longer the habit continues, the more severe the dental changes can become. While thumb sucking is a natural reflex for infants, prolonged thumb sucking beyond toddlerhood significantly increases the risk of developing buck teeth.
At What Age Does Thumb Sucking Become Problematic?
Thumb sucking is generally harmless in infants and toddlers under the age of 2. Most children outgrow the habit naturally between ages 2 and 4. However, if thumb sucking persists beyond age 4 or continues into the time when permanent teeth begin to erupt (around age 6), it becomes problematic.
Prolonged sucking can alter the shape of the developing jaw and affect the position of incoming adult teeth, leading to noticeable protrusion. Pediatricians and dentists often recommend gentle behavioral interventions around age 3 or 4 to help children gradually stop the habit before it impacts dental development.
How Does Duration of Sucking Affect Tooth Movement?
The length of time a child sucks their thumb each day directly impacts the severity of tooth movement. A child who only sucks their thumb occasionally may not experience significant dental changes, while one who engages in the habit for hours especially during sleep applies constant pressure to the upper front teeth and palate.
This continuous force can gradually push the teeth outward and cause the jaw to develop abnormally. Duration is often more important than intensity; even gentle thumb sucking over long periods can lead to buck teeth. Limiting and eventually eliminating the habit early is key to preventing misalignment. Traditional metal braces are highly effective for correcting severe misalignment and bite issues
How Does Pacifier Use Lead to Buck Teeth Development?
While pacifiers can be a helpful soothing tool for infants, prolonged use can have similar effects on dental development as thumb sucking. Frequent pacifier use beyond infancy can cause the upper front teeth to tilt outward and the lower teeth to angle inward, resulting in a malocclusion.
The sucking motion changes the shape of the mouth over time, particularly if a pacifier is used throughout the day and during sleep. If a child continues to use a pacifier after the age of 2–3, it increases the risk of developing buck teeth and other bite problems, requiring orthodontic correction later.
What Types of Pacifiers Cause the Most Damage?
Not all pacifiers have the same impact on dental health. Traditional, rounded pacifiers tend to exert more pressure on the upper teeth and palate, increasing the risk of misalignment. In contrast, orthodontic pacifiers are designed to minimize dental damage by distributing pressure more evenly across the mouth.
However, even orthodontic pacifiers can cause buck teeth if used excessively or beyond the recommended age. The most damaging pacifiers are those used frequently after age 3, regardless of their design. Limiting usage time and choosing orthodontic-friendly options can reduce the likelihood of buck teeth caused by pacifier use.
When Should Parents Stop Pacifier Use to Prevent Buck Teeth?
To prevent buck teeth and other dental issues, most pediatric dentists recommend that pacifier use be discontinued by age 2 or, at the latest, by age 3. By this time, the baby teeth are fully erupted, and the jaw is in a crucial stage of development.
Continued pacifier use past this age can negatively affect how the teeth align and how the jawbone grows. Gradual weaning strategies, such as limiting pacifier use to bedtime or introducing comfort alternatives, can help children let go of the habit without distress. Early weaning significantly reduces the need for orthodontic treatment later.
Why Does Tongue Thrusting Cause Forward Tooth Movement?
Tongue thrusting is a condition where the tongue pushes against or between the front teeth during swallowing, speaking, or at rest. This repetitive pressure causes the front teeth, particularly the upper ones, to move outward over time, leading to buck teeth.
Tongue thrusting often starts in early childhood and may be linked to prolonged thumb sucking, bottle feeding, or enlarged tonsils. Because the tongue is a strong muscle, its persistent pressure is enough to shift tooth position, especially during critical stages of dental and jaw development. Left untreated, tongue thrusting can cause long-term bite issues and speech problems.
How Can Parents Identify Tongue Thrusting in Children?
Parents can look for several signs of tongue thrusting in their children. Common indicators include an open bite (where the front teeth don’t touch when the mouth is closed), difficulty pronouncing certain sounds (especially “s” and “z”), and visible tongue movement between the teeth during swallowing or speaking.
Children who frequently keep their mouths open or breathe through their mouths may also be more prone to this habit. If tongue thrusting is suspected, a consultation with a pediatric dentist or speech therapist can help diagnose the issue and determine if intervention is needed to prevent buck teeth.
What Triggers Develop Tongue Thrusting Habits?
Several factors can trigger the development of tongue thrusting habits. Prolonged thumb sucking or pacifier use is a common contributor, as these habits can alter tongue posture. Enlarged tonsils or adenoids, allergies, or chronic nasal congestion can also lead children to develop mouth-breathing habits that encourage tongue thrusting.
Additionally, some children may adopt this pattern due to improper bottle or spoon-feeding techniques during infancy. Identifying and addressing these triggers early through medical treatment or behavioral therapy can prevent tongue thrusting from becoming a long-term habit that leads to buck teeth or other dental issues.
How Do Lip Habits Contribute to Dental Protrusion?
Lip habits, such as lip sucking or lip biting, can subtly but steadily influence the alignment of a child’s teeth. These habits often involve repetitive actions that place uneven pressure on the teeth and jaw. For instance, children who suck their lower lip tend to push their upper teeth forward while pulling their lower teeth backward.
Over time, this creates an exaggerated overjet or buck teeth. Lip biting, particularly when done regularly or as a response to stress, can also cause misalignment. Though these habits may seem minor, they can have a lasting impact on dental development.
What Effect Does Lip Biting Have on Tooth Position?
Lip biting, especially when frequent or habitual, exerts unnatural forces on the front teeth. When a child repeatedly bites their lower lip, the upper teeth may be pushed forward while the lower teeth get forced inward, leading to protrusion and an uneven bite.
This type of repetitive behavior often becomes unconscious and can occur during times of stress or concentration.
Over time, the constant pressure on the teeth alters their natural position, increasing the likelihood of developing buck teeth. Early intervention through behavioral guidance or orthodontic consultation can help stop the habit before it causes significant dental changes.
How Does Lower Lip Sucking Create Buck Teeth?
Lower lip sucking involves the child placing their lower lip behind the upper front teeth, often during rest or while sleeping. This habit can place backward pressure on the lower teeth and forward pressure on the upper teeth, creating a classic buck teeth appearance.
Over time, the continuous motion and pressure cause the teeth to shift and the bite to open up in the front. Children may develop this habit as a soothing behavior or in response to anxiety. Recognizing and addressing lower lip sucking early through behavior modification or orthodontic guidance can prevent it from permanently altering tooth alignment.
What Developmental Issues Cause Buck Teeth in Children?
In addition to genetics and habits, developmental issues are a significant contributor to buck teeth in children. These issues typically arise during critical growth phases when the jaws and teeth are forming and shifting into position. Imbalances in jaw development, early loss of baby teeth, or problems with the way teeth erupt can all lead to misalignment.
Because the development of the face, jaw, and teeth is closely interconnected, even small disruptions can cause the front teeth to protrude. Understanding these developmental causes is essential for early intervention, which can often reduce the need for extensive orthodontic treatment later. Prolonged thumb sucking in children can lead to buck teeth and other orthodontic problems
How Does Jaw Growth Imbalance Lead to Tooth Protrusion?
One of the most common developmental causes of buck teeth is an imbalance in jaw growth. The upper and lower jaws are meant to grow in harmony, creating a balanced bite. However, when the upper jaw grows too much or the lower jaw doesn’t grow enough, it causes the upper front teeth to stick out.
These discrepancies often become noticeable during growth spurts in childhood or adolescence. Jaw imbalances not only affect appearance but can also impact speech, chewing, and self-esteem. Orthodontic treatment, sometimes in combination with growth modification appliances can help guide jaw development and prevent worsening overbites.
What Happens When the Upper Jaw Grows Too Much?
When the upper jaw (maxilla) grows disproportionately faster or larger than the lower jaw, it can cause the upper front teeth to protrude significantly, resulting in buck teeth. This overdevelopment creates a space where the upper teeth no longer align with the lower teeth, leading to a noticeable overjet.
This kind of skeletal imbalance is often genetic but can be worsened by environmental factors like prolonged thumb sucking. In moderate to severe cases, orthodontic appliances such as headgear or functional appliances may be used during growth phases to slow or redirect jaw growth, improving both function and aesthetics.
How Does Underdeveloped Lower Jaw Cause Buck Teeth?
A small or underdeveloped lower jaw (mandibular retrognathia) can also lead to the appearance of buck teeth, even if the upper jaw is normal in size.
Because the lower jaw is positioned further back than it should be, the upper teeth appear to protrude forward. This imbalance can be congenital or occur due to growth disturbances during early childhood.
It may also affect breathing, especially if paired with mouth-breathing habits. Functional orthodontic appliances are often used in growing children to encourage forward development of the lower jaw and to reduce or eliminate the appearance of buck teeth over time.
Why Do Premature Tooth Loss Patterns Create Buck Teeth?
Premature loss of baby teeth disrupts the natural timing and spacing needed for adult teeth to erupt properly. When primary teeth fall out too early, the surrounding teeth can drift into the open space, which can block or redirect the eruption of permanent teeth. This crowding can push front teeth forward or cause them to erupt at odd angles, creating an overjet.
These types of developmental issues are preventable in many cases through regular dental checkups and timely intervention. Dentists may recommend space maintainers or early orthodontic evaluations to guide proper tooth alignment and avoid protrusion.
How Does Early Loss of Baby Teeth Affect Alignment?
Baby teeth serve as placeholders for permanent teeth, helping to maintain proper spacing in the jaw. When a baby tooth is lost too early often due to trauma or decay the teeth around the gap can drift into the empty space. This drifting causes crowding and misalignment, which can force new teeth to erupt in improper positions.
If the front teeth erupt without enough space, they may protrude outward, resulting in buck teeth. The earlier the loss occurs, the greater the risk of alignment problems. This is why preserving baby teeth until their natural shedding time is so critical.
What Role Do Space Maintainers Play in Prevention?
Space maintainers are small orthodontic devices used to preserve the space left by a prematurely lost baby tooth. They prevent neighboring teeth from shifting into the vacant area, allowing the permanent tooth to erupt in its proper place.
Without a space maintainer, teeth can drift and cause crowding or push the front teeth outward, resulting in buck teeth or other malocclusions. These devices are simple, painless, and highly effective when applied early.
Regular dental visits help identify when a space maintainer is needed, making it an essential tool in preventing alignment issues before they require extensive orthodontic treatment.
How Do Eruption Problems Lead to Buck Teeth Formation?
Tooth eruption is a complex developmental process, and any disruption in this sequence can lead to misalignment. Teeth that erupt too early, too late, or in the wrong position can push neighboring teeth out of place. When the upper front teeth erupt at an angle or are forced forward due to lack of space, it can result in buck teeth.
Additionally, abnormal eruption patterns often lead to crowded or rotated teeth, which further complicate the bite. Monitoring a child’s dental development with regular checkups ensures that eruption issues are identified and treated before they lead to severe protrusion.
What Happens When Teeth Erupt in Wrong Positions?
When teeth erupt in improper positions, they can disrupt the natural alignment of the dental arch. For example, if a permanent tooth comes in behind or in front of where it should, it can push other teeth forward or backward. This may result in buck teeth, crowding, or even crossbites.
These positional issues are often caused by factors like retained baby teeth, early tooth loss, or lack of jaw space. In many cases, early orthodontic treatment such as braces or expansion appliances can correct these problems while the mouth is still growing, reducing the risk of long-term misalignment.
How Do Impacted Teeth Cause Forward Protrusion?
Impacted teeth are those that fail to erupt fully into the mouth, often due to crowding or obstruction by other teeth. While they typically stay hidden beneath the gums, their presence can still affect surrounding teeth.
Impacted teeth, especially canines, can push adjacent teeth forward as they attempt to erupt, contributing to the appearance of buck teeth. They may also cause misalignment of the entire dental arch. Diagnosis often requires X-rays or panoramic imaging.
Early detection and treatment such as creating space or surgically exposing the impacted tooth can help redirect its eruption and prevent forward protrusion. Correcting a severe overbite often requires orthognathic jaw surgery in combination with braces
Which Medical Conditions Are Linked to Buck Teeth Development?
Several medical conditions can directly or indirectly influence the development of buck teeth in children. Issues such as breathing disorders, allergies, and hormonal imbalances can interfere with normal jaw and dental development.
These conditions often impact how a child breathes, sleeps, or growth factors that are critically connected to the formation and alignment of teeth. When these medical conditions go undiagnosed or untreated, they can contribute to forward tooth protrusion, improper bite formation, and jaw discrepancies.
Understanding the medical factors that influence dental structure can help parents and caregivers take early steps toward prevention and timely treatment.
How Do Breathing Disorders Contribute to Buck Teeth?
Breathing disorders, especially those that affect nasal airflow, play a significant role in altering the growth of the jaw and teeth. Children with chronic breathing problems tend to adapt by mouth breathing, which changes tongue posture and jaw muscle function.
This often results in the upper jaw developing more vertically and narrowing over time, causing the upper front teeth to protrude. Additionally, improper breathing can lead to an open bite or longer facial structure.
These skeletal changes are particularly problematic during key developmental years. Identifying and treating the underlying breathing disorder can help prevent or minimize buck teeth formation.
What Role Does Mouth Breathing Play in Tooth Protrusion?
Mouth breathing is one of the most common contributors to buck teeth related to breathing disorders. When a child breathes through their mouth instead of their nose often due to nasal blockages or allergies it changes the natural resting position of the tongue.
Instead of pressing gently against the roof of the mouth, the tongue rests low, failing to support the upper jaw’s width. This leads to a narrow palate, elongation of the face, and outward growth of the upper front teeth. Over time, this creates an overjet or buck teeth. Addressing mouth breathing early through ENT evaluation or allergy treatment is essential.
How Do Enlarged Adenoids Affect Dental Development?
Enlarged adenoid/lymphatic tissue located behind the nasal passages can block airflow, forcing a child to breathe through their mouth. Chronic mouth breathing due to enlarged adenoids can significantly affect jaw growth and dental alignment.
The condition promotes vertical facial growth and a narrow, high-arched palate, pushing the upper front teeth forward. It may also cause speech issues and lead to sleep-disordered breathing.
Many cases of unexplained buck teeth or open bites in children are later traced back to undiagnosed adenoid hypertrophy. An evaluation by an ENT specialist and, if needed, surgical removal can help restore nasal breathing and support proper facial development.
Why Do Allergies Lead to Buck Teeth Formation?
Chronic allergies often result in nasal congestion, prompting children to breathe through their mouths. Like with other breathing disorders, mouth breathing triggered by allergies disrupts normal facial and dental development.
Over time, it can narrow the upper jaw, misalign the bite, and push the upper front teeth forward. Children with long-term untreated allergies may also develop habits like tongue thrusting or lip sucking, which further contribute to dental protrusion.
Because allergies are a long-term condition, they need to be managed medically to prevent recurring effects on jaw growth. Allergy testing, medication, and environmental control can all help reduce the risk of buck teeth.
How Do Chronic Nasal Congestion Patterns Affect Teeth?
Children with chronic nasal congestion due to allergies, sinus infections, or environmental irritants are at a much higher risk of developing buck teeth. When the nose is consistently blocked, the child adapts by breathing through the mouth.
This change in breathing pattern can lead to incorrect tongue placement, narrow palate development, and an imbalanced bite. Furthermore, nasal congestion may result in poor sleep, affecting overall growth patterns, including the development of the jaw.
Prolonged congestion during critical growth periods can result in permanent changes to the dental arch, including forward-tilting front teeth. Effective treatment of congestion is key to preserving dental health.
What Connection Exists Between Allergies and Jaw Growth?
Allergies can influence jaw growth through both mechanical and biological mechanisms. Mechanically, they cause nasal blockages, leading to chronic mouth breathing, which alters the normal muscle function of the face and jaw.
This adaptation often results in a longer facial structure, narrower upper jaw, and outward movement of the upper teeth. Biologically, inflammatory processes associated with allergies may interfere with normal growth signals, subtly affecting bone development over time.
If left unmanaged, allergies can lead to long-term structural changes in the face, resulting in buck teeth or open bites. Treating allergies early helps ensure that jaw growth follows its normal trajectory.
How Do Hormonal Imbalances Influence Tooth Positioning?
Hormonal imbalances especially during growth spurts in childhood or puberties affect the timing and pattern of bone development, including the jaws and teeth. Conditions such as growth hormone deficiency, hypothyroidism, or early puberty can all lead to discrepancies in jaw size or bone density.
These imbalances may cause one part of the jaw to grow faster than the other, resulting in misaligned teeth or overjets. Since hormonal factors can alter how and when teeth erupt, they can create crowding or excessive spacing that contributes to buck teeth. Pediatricians and orthodontists often work together to manage such cases effectively.
What Effect Do Growth Hormones Have on Dental Structure?
Growth hormones are critical for normal bone development, including that of the face and jaw. If a child has a deficiency or excess of growth hormone, it can lead to structural imbalances. For instance, too little growth hormone may result in an underdeveloped lower jaw, causing the upper teeth to appear more prominent.
Conversely, excess growth hormone (as seen in rare conditions like gigantism) may cause disproportionate jaw growth. Either scenario can result in buck teeth or other bite issues. Monitoring growth patterns and correcting hormonal imbalances early can help maintain healthy dental and skeletal development.
How Do Thyroid Disorders Impact Tooth Development?
Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can disrupt the timing and quality of tooth development. In hypothyroidism, delayed growth and late tooth eruption are common, which can result in misalignment or crowding that pushes the front teeth outward. In contrast, hyperthyroidism may accelerate growth and tooth eruption, sometimes before the jaw is fully ready, leading to spacing and protrusion issues.
Thyroid hormones influence metabolism, bone growth, and tooth formation, making their balance essential for proper dental development. Children with thyroid conditions should receive regular dental checkups to monitor for early signs of misalignment, including buck teeth. We provide comprehensive dental correction , from orthodontics to restorative work, all in one place
What Environmental Factors Cause Buck Teeth to Develop?
Environmental factors are often overlooked but play a crucial role in the development of buck teeth. Unlike genetic or medical causes, these influences are usually related to a child’s daily habits and surroundings. The way a baby is fed, how they sleep, and even what they eat can subtly but significantly alter the way their teeth and jaws grow.
Poor bottle-feeding techniques, improper sleep posture, and nutritional deficiencies can all create conditions that encourage tooth protrusion. Because these factors are modifiable, understanding and addressing them early can prevent long-term dental problems and reduce the need for orthodontic correction.
How Does Bottle Feeding Technique Affect Tooth Alignment?
Bottle feeding, when done incorrectly, can negatively affect the alignment of a child’s teeth and jaw. Poor technique such as holding the bottle at the wrong angle or allowing prolonged feeding beyond infancy can lead to the development of buck teeth.
This happens because the suction motion used during bottle feeding mimics thumb sucking to a degree and, over time, can push the upper front teeth outward if not managed properly.
Additionally, bottle-fed babies often rest with the bottle in their mouth for extended periods, especially during sleep, which contributes to abnormal oral muscle patterns and misaligned teeth.
What Bottle Positions Promote Buck Teeth Formation?
Holding the bottle in a horizontal or upward-tilted position while feeding can encourage the baby to exert more suction force than necessary, similar to thumb sucking. This creates forward pressure on the upper jaw and teeth, encouraging them to protrude.
When babies lie flat on their backs or feed while reclined too far, the tongue and mouth muscles have to compensate, potentially shifting the developing jaw structure over time. The ideal bottle-feeding position is semi-upright, with the bottle tilted just enough to allow milk flow without requiring excessive sucking effort. Proper posture helps maintain natural oral development.
How Long Should Bottle Feeding Continue Safely?
Pediatric dentists generally recommend weaning from the bottle by 12 to 18 months of age to minimize the risk of dental issues like buck teeth. Prolonged bottle feeding especially when it continues past age 2 can interfere with jaw and tooth development.
This is because extended bottle use keeps the oral muscles in a “sucking” pattern longer than necessary, which may push the front teeth forward. Also, if bottle use continues during sleep, it can combine with mouth breathing and improper tongue posture to further misalign the teeth. Transitioning to a cup early promotes healthier oral habits and reduces protrusion risk.
Why Do Sleep Position Habits Contribute to Dental Problems?
Sleep positions can significantly influence a child’s facial growth and dental development, particularly during early childhood when bones are still malleable. When a child frequently sleeps in positions that apply uneven pressure to the jaw such as on the stomach or with their face pressed against a pillow it can cause the jaw to grow asymmetrically or push the teeth out of alignment. Over time, this pressure can lead to forward tilting of the upper teeth, resulting in buck teeth. While sleep positioning is often accidental or habitual, correcting it early can support better facial symmetry and dental alignment.
How Does Sleeping on Stomach Affect Jaw Development?
Stomach sleeping can cause the head and jaw to be pressed into the pillow, applying uneven pressure on the facial bones. This often results in flattening of one side of the jaw or even misdirected jaw growth, which in turn can cause teeth to shift out of alignment. When pressure is consistently applied to the front of the face during sleep, the upper jaw may narrow or the front teeth may be pushed forward, contributing to buck teeth. Encouraging back or side sleeping, especially with a supportive pillow, helps reduce these risks and promotes balanced jaw development.
What Pillow Types Can Influence Tooth Positioning?
The type of pillow a child uses can influence how pressure is distributed across their face during sleep. Very soft or overly large pillows may allow the head to sink too deeply, pressing against the lower face and altering jaw growth over time. Conversely, firm, ergonomically designed pillows help keep the neck and head aligned without excessive facial pressure. Memory foam pillows with contoured shapes can be especially helpful in maintaining a healthy sleeping posture. For toddlers and young children, choosing a pillow that supports the head without pushing the jaw forward or sideways is important for healthy dental development.
How Do Dietary Factors Influence Buck Teeth Development?
Dietary habits, particularly in the early years, can influence both tooth eruption and jaw growth. A balanced diet supports the proper mineralization of teeth and the healthy development of jawbones. Deficiencies in nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus can weaken the teeth and delay their eruption, potentially causing them to come in crooked or at incorrect angles. Likewise, a diet lacking in chewy or hard foods may under-stimulate the jaw muscles, limiting proper growth and development. Conversely, including a variety of nutrient-dense and appropriately textured foods can help the jaw form symmetrically, reducing the risk of buck teeth.
What Role Does Calcium Deficiency Play in Tooth Formation?
Calcium is essential for tooth and bone development, and a deficiency during early childhood can affect how teeth grow and align. Without enough calcium, the enamel may be weaker, and the roots and jawbones may not develop to their full strength or size. This can delay the eruption of teeth or cause them to emerge at odd angles, contributing to protrusion or spacing issues. Additionally, weak jawbones may not properly support tooth alignment, allowing teeth to drift forward. Ensuring children receive sufficient calcium through milk, yogurt, leafy greens, or fortified foods helps reduce the likelihood of developing buck teeth due to nutritional deficiencies.
How Do Hard Foods Affect Jaw Development Patterns?
Chewing hard or fibrous foods like raw vegetables, whole fruits, and tough meat stimulates jaw muscles and promotes strong, balanced jaw growth. In contrast, soft modern diets, which include many pureed or processed foods, can lead to underdeveloped jaws and narrow palates. When the jaw doesn’t grow wide enough to accommodate all the teeth, crowding occurs, often pushing the front teeth forward into a buck teeth position. Including harder foods in a child’s diet encourages natural strengthening of the chewing muscles and bone structure, supporting proper alignment and reducing the risk of dental protrusion.
What Trauma-Related Causes Lead to Buck Teeth?
While genetics and habits often get the most attention, trauma is another significant factor in the development of buck teeth. Injuries to the face or mouth during early childhood, especially while permanent teeth and jaw structures are still developing can disrupt the alignment and position of teeth. These accidents may cause teeth to shift, loosen, or erupt abnormally. From everyday falls to sports-related injuries, trauma can lead to long-term dental issues if not addressed promptly. Understanding how trauma affects tooth development and the importance of early dental evaluation after an injury is key to preventing permanent dental protrusion and misalignment.
How Do Facial Injuries Result in Tooth Protrusion?
Facial injuries, particularly those that involve direct impact to the mouth or jaw can lead to buck teeth in a variety of ways. Trauma can push teeth out of position or damage the bone that supports them. If an injury occurs before the permanent teeth have erupted, it may disturb the alignment path, causing those teeth to emerge at incorrect angles. In some cases, teeth may be loosened or tilted forward due to force, leading to visible protrusion. Additionally, trauma can affect jaw development if it damages the growth plates, potentially causing skeletal imbalance. Timely evaluation helps reduce long-term misalignment.
What Types of Accidents Most Commonly Cause Buck Teeth?
The most common accidents that lead to buck teeth are childhood falls, sports injuries, and bicycle or playground accidents. Toddlers learning to walk frequently fall forward, and if they land on their face, the impact can damage developing front teeth. School-aged children are especially at risk for dental trauma during contact sports like football, basketball, and hockey if proper mouthguards aren’t used. Bicycle falls and scooter accidents also commonly result in injuries to the face and mouth. When these incidents involve the upper front teeth, they can cause displacement or changes in eruption patterns that lead to permanent protrusion.
How Do Sports Injuries Affect Long-term Dental Alignment?
Sports injuries, particularly in contact sports, can have lasting effects on a child’s dental alignment. Blows to the face can knock teeth out of position or cause fractures in the jaw that alter how future teeth erupt. Even if the immediate injury seems minor, the trauma can shift teeth forward or cause subtle changes in jaw structure. Without prompt dental care, the damage may worsen as the child grows. Using a custom-fitted mouthguard during sports is one of the most effective ways to protect against this. Long-term alignment problems from sports trauma may require braces or other orthodontic intervention.
Why Does Dental Trauma During Development Cause Problems?
Dental trauma during development is particularly problematic because a child’s jawbones, gums, and teeth are still forming. Any injury sustained before or during the eruption of permanent teeth can disrupt their normal path, leading to misalignment or buck teeth. For example, if a baby tooth is knocked out prematurely or the surrounding gum tissue is damaged, the permanent tooth underneath may erupt too early or at an abnormal angle. Trauma can also damage the bone or tooth buds beneath the gumline, altering the growth and spacing of future teeth. Early evaluation and monitoring are crucial to minimizing long-term effects.
How Do Childhood Falls Impact Permanent Tooth Position?
Childhood falls, especially in toddlers and preschoolers, are one of the most frequent causes of dental trauma. When a child falls forward and hits their mouth, the baby teeth can be displaced, loosened, or driven into the gums, potentially damaging the developing permanent teeth beneath. Even if the baby tooth stays in place, the root structure may be affected, which can influence the way the permanent tooth erupts later. These falls can lead to improper angling of the adult teeth, resulting in buck teeth or other alignment problems. Regular dental monitoring after a fall helps ensure proper tooth development.
What Role Does Early Dental Intervention Play After Trauma?
Immediate dental intervention after trauma is critical in reducing the risk of long-term issues like buck teeth. When a child experiences a fall or injury involving their mouth, a dentist can assess not just the visible damage but also potential risks to underlying tooth buds and jaw structures. Interventions may include repositioning a displaced tooth, using a space maintainer, or scheduling follow-up X-rays to monitor the development of permanent teeth. Acting quickly can prevent misaligned eruptions or bone growth abnormalities. In many cases, early treatment reduces or even eliminates the need for more extensive orthodontic work in the future. We analyze famous smiles to help patients articulate the look they want to achieve
How Do Age-Related Factors Contribute to Buck Teeth Formation?
Age plays a crucial role in the development of buck teeth, as the jaw and teeth undergo significant changes from infancy through adulthood. Different growth stages present unique vulnerabilities that can lead to or worsen dental protrusion. During childhood, the jaws are still forming, making them more susceptible to influence from habits, genetics, and environmental factors. Adolescents may experience growth spurts that affect bite and tooth alignment, while adults may develop buck teeth due to bone density changes or tooth loss. Understanding how age impacts dental development helps in early diagnosis, timely intervention, and long-term prevention of protrusion.
What Happens During Critical Development Periods?
Critical development periods, such as early childhood and adolescence, are when the jaws and teeth grow rapidly and can be easily influenced. If improper habits like thumb sucking or mouth breathing persist during these windows, they can distort jaw growth and tooth alignment. Additionally, eruption timing of baby and permanent teeth during these periods is vital. Delays or early losses can lead to misalignment and forward tooth movement. Orthodontic evaluations are most effective when timed with these developmental phases, allowing dental professionals to intervene early and use natural growth patterns to guide the teeth into proper alignment.
How Do Growth Spurts Affect Tooth Positioning?
During growth spurts, especially in preteens and teens, the jawbones grow rapidly. If this growth is uneven such as the upper jaw growing faster than the lower it can result in protruding front teeth or an overbite. These spurts also coincide with the eruption of permanent teeth, and without enough space, the front teeth may be pushed outward. Growth spurts can both cause and worsen buck teeth if bite issues or spacing problems are already present. Orthodontists often time braces or growth-modifying appliances around these periods to leverage the body’s natural development in correcting misalignment.
What Changes Occur During Adolescent Development?
Adolescence brings hormonal changes and rapid skeletal growth, including significant changes in the jaw structure. If the upper and lower jaws don’t grow in harmony, it can cause an overjet or buck teeth. Additionally, this is the period when the final permanent teeth (excluding wisdom teeth) erupt, and any lack of space can force the front teeth forward. Poor posture, diet, or undiagnosed habits like tongue thrusting may also appear or worsen during adolescence, further affecting alignment. Addressing orthodontic concerns during these years is often ideal, as treatments can work with the body’s natural growth for more effective results.
Why Do Some Adults Develop Buck Teeth Later in Life?
Although buck teeth are often associated with childhood, adults can also develop protrusion due to aging, lifestyle changes, or dental neglect. As we age, bone density decreases, and the support structures around teeth weaken. This can lead to tooth shifting, especially if there’s preexisting crowding or past trauma. Additionally, adults may lose teeth due to decay or gum disease, and the remaining teeth can drift into the empty spaces, pushing the front teeth forward. Others may develop buck teeth because they never treated orthodontic issues earlier in life. Proper dental maintenance and early correction can help prevent these age-related changes.
How Does Aging Affect Jaw Bone Density and Tooth Position?
Aging naturally causes a reduction in jawbone density, especially if the individual has gum disease or osteoporosis. This bone loss weakens the support system for teeth, allowing them to shift from their original positions. In many cases, the front teeth move forward slightly, creating the appearance of buck teeth or worsening an existing overjet. Additionally, with less bone mass, the jaw can shrink in size, altering the bite and facial structure. This can lead to spacing issues and misalignment. Regular dental checkups, proper nutrition, and bone density monitoring can help manage these age-related changes and maintain healthy tooth positioning.
What Role Does Tooth Loss Play in Adult Buck Teeth?
Tooth loss particularly of molars can cause the remaining teeth to drift out of place. When back teeth are lost, the pressure from chewing shifts forward, which can push the front teeth outward. This chain reaction often leads to buck teeth or other alignment issues. Gaps from missing teeth also cause neighboring teeth to tilt or rotate, disrupting the bite and jaw symmetry. Without replacement (e.g., implants or bridges), the changes can become permanent. Adults experiencing tooth loss should seek timely dental intervention to prevent shifting and maintain a proper bite, preserving both aesthetics and oral function.
Which Orthodontic Issues Previously Cause Buck Teeth?
Certain untreated orthodontic conditions can directly result in the formation of buck teeth over time. These include overbites, crossbites, crowding, and jaw size discrepancies. If not corrected in childhood or adolescence, these issues often worsen with age, leading to more pronounced tooth protrusion. Some patients may not notice the shift until it becomes visible or starts causing discomfort. Others may have had orthodontic treatment but failed to wear retainers, causing relapse. Addressing these foundational bite problems early is key to preventing or minimizing the development of buck teeth later in life.
How Do Untreated Bite Problems Lead to Protrusion?
Bite problems such as overbites, underbites, and crossbites can cause improper contact between the upper and lower teeth. When the bite is misaligned, the jaw muscles may compensate in ways that push the upper front teeth forward. Over time, this leads to buck teeth, especially if the issue is left untreated during growth phases. The longer the imbalance goes uncorrected, the harder it becomes to fix due to bone adaptation. Early diagnosis and orthodontic treatment can guide the teeth and jaws into better alignment, reducing stress on the jaw and preventing dental protrusion.
What Effect Does Overbite Have on Tooth Movement?
An overbite occurs when the upper front teeth overlap the lower front teeth excessively. If left untreated, the continuous pressure from the upper jaw can cause the front teeth to tilt outward, resulting in buck teeth. Overbites are one of the most common bite issues seen in children and adolescents, and they often worsen with age if not corrected. Additionally, overbites can cause wear on the lower teeth, jaw pain, and speech issues. Braces or other orthodontic appliances can reposition the jaws and reduce the overbite, preventing the associated forward movement of the front teeth.
How Do Crossbite Issues Contribute to Buck Teeth?
A crossbite occurs when the upper and lower teeth do not align properly, either at the front or back of the mouth. This misalignment forces the jaw to compensate during chewing and speaking, often causing uneven pressure on certain teeth. Over time, the upper front teeth may begin to protrude if the crossbite causes the lower jaw to move forward or sideways. This leads to abnormal tooth wear and forward positioning. Correcting a crossbite early especially in children can help guide jaw development and prevent related issues like buck teeth. Treatments may include braces or palatal expanders.
Why Does Crowding Result in Forward Tooth Movement?
Dental crowding occurs when there is not enough space in the jaw for all the teeth to align properly. In crowded mouths, the pressure from erupting teeth can force some to strengthen the upper front ones to move forward or outward, resulting in buck teeth. Crowding is more common in people with smaller jaws or large teeth and often starts during the transition from baby teeth to adult teeth. Without early orthodontic treatment, crowding worsens as more teeth erupt. Braces, spacers, or expansion appliances can create room in the jaw, aligning the teeth and preventing forward protrusion.
How Do Small Jaws Create Crowding and Protrusion?
A small or narrow jaw cannot accommodate the full set of adult teeth, leading to crowding. As the permanent teeth erupt, they compete for limited space and may overlap, rotate, or push forward. The front teeth, especially, are prone to protruding outward, resulting in the appearance of buck teeth. Small jaw size is often genetic but can also be influenced by childhood habits like mouth breathing. Orthodontists can intervene with treatments like palatal expanders to widen the jaw and create more room for teeth to align correctly, reducing the chances of both crowding and dental protrusion.
What Happens When Wisdom Teeth Cause Crowding?
Wisdom teeth, or third molars, usually erupt in the late teens or early 20s. In many people, there’s not enough room in the jaw for these extra teeth, leading to impaction or shifting of existing teeth. The forward pressure from erupting wisdom teeth can cause the front teeth especially on the lower jaw to crowd, tilt, or move outward. This crowding can worsen or even cause buck teeth in people who previously had straight teeth. Dentists often recommend removal of wisdom teeth before they fully erupt if crowding is likely, especially in patients with a history of orthodontic treatment.
What Modern Lifestyle Factors Contribute to Buck Teeth?
In today’s fast-paced world, modern lifestyle habits are playing an increasing role in the development of buck teeth often in ways we don’t immediately recognize. Extended use of digital devices, sedentary behavior, increased stress, and poor posture are all contributing to changes in jaw development and oral health. Unlike genetic or early childhood factors, these influences often emerge gradually over time, but their impact on dental alignment can be significant. These habits affect facial muscles, tongue posture, breathing patterns, and even the way we chew or clench our jaws ultimately leading to subtle but progressive forward movement of the front teeth.
How Do Digital Device Habits Affect Jaw Development?
Excessive use of digital devices, phones, tablets, and computers encourages prolonged forward head posture, which can subtly alter the way the jaw grows and aligns. When the head juts forward, the lower jaw tends to shift backward and down, putting strain on the jaw muscles and changing the bite. Over time, this misalignment can cause the upper front teeth to protrude, particularly during childhood and adolescence when the facial bones are still growing. Additionally, device use is often associated with mouth breathing and inactive facial muscles, both of which contribute to improper jaw development and potential buck teeth formation.
What Role Does Poor Posture Play in Dental Problems?
Poor posture, especially forward head posture (FHP), directly affects the alignment of the jaw, neck, and spine. When the head is positioned forward as it often is while looking at screens the jaw is pulled down and back, which can disturb the balance of muscle forces around the face. This misalignment leads to compensatory movements that place pressure on the upper front teeth, causing them to shift outward over time. For growing children and teens, this pressure can become permanent, resulting in buck teeth. Encouraging ergonomic habits and body awareness, especially during screen time, can significantly reduce this risk.
How Do Screen Time Habits Impact Oral Development?
Long hours of screen time whether for school, work, or entertainment can have subtle but significant effects on oral and facial development, especially in children. Excessive screen use often leads to slouched sitting, mouth breathing, and inactive facial muscles. These habits interfere with the proper development of the palate, jaw, and bite. Additionally, kids engrossed in screens may adopt poor swallowing patterns or rest their tongue improperly, both of which contribute to the forward movement of the upper teeth. Balancing screen time with physical activity, proper posture, and regular breaks can help preserve normal jaw growth and dental alignment.
Why Do Stress-Related Habits Lead to Buck Teeth?
Chronic stress affects not only mental health but also oral health and tooth positioning. Many people unconsciously respond to stress with habits such as teeth grinding (bruxism), jaw clenching, lip biting, or tongue thrusting all of which put excess pressure on the teeth and jaw. Over time, these behaviors can wear down enamel, push teeth out of alignment, and contribute to the development or worsening of buck teeth. Stress-related habits often go unnoticed until they start causing pain, tension, or visible dental changes. Recognizing and managing these habits through lifestyle changes, dental splints, or therapy is key to preventing long-term misalignment.
How Does Teeth Grinding Affect Tooth Position Over Time?
Teeth grinding, or bruxism, puts constant pressure on the teeth, especially during sleep. This repetitive motion gradually alters the bite and shifts teeth sometimes causing them to tilt forward or crowd. While grinding is most commonly associated with tooth wear, it also contributes to jaw muscle overuse and joint strain, which can pull the jaw into unnatural positions. Over months or years, this leads to changes in tooth alignment, including protrusion of the front teeth. Custom night guards, stress management techniques, and regular dental monitoring can help reduce grinding and preserve proper alignment.
What Connection Exists Between Anxiety and Dental Issues?
Anxiety and chronic stress often manifest physically through unconscious oral habits such as clenching the jaw, grinding teeth, or pressing the tongue against the front teeth. These behaviors increase pressure on the dental arch and jaw joint, which can gradually lead to misalignment or protrusion of the front teeth. Anxiety can also contribute to mouth breathing and poor sleep posture, both of which impact jaw development. Over time, these small habits accumulate, potentially resulting in buck teeth or TMJ disorders. Addressing the root causes of anxiety, along with dental interventions, can reduce the physical effects on oral health.
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h3″ question-0=”What is the most common cause of buck teeth in children?” answer-0=”Thumb sucking and prolonged pacifier use are the most common causes.” image-0=”” headline-1=”h3″ question-1=”Can buck teeth be prevented if parents intervene early?” answer-1=”Yes, early intervention can often prevent or reduce severity.” image-1=”” headline-2=”h3″ question-2=”At what age do buck teeth typically start developing?” answer-2=”They usually begin to show between ages 4 and 7.” image-2=”” headline-3=”h3″ question-3=”Are buck teeth more common in boys or girls?” answer-3=”They occur at similar rates in both boys and girls.” image-3=”” headline-4=”h3″ question-4=”How quickly can buck teeth develop once they start forming?” answer-4=”They can become noticeable within a few months, depending on the cause.” image-4=”” headline-5=”h3″ question-5=”Can breastfeeding help prevent buck teeth development?” answer-5=”Yes, breastfeeding may help reduce the risk by promoting proper jaw development.” image-5=”” headline-6=”h3″ question-6=”What percentage of buck teeth cases are caused by genetics?” answer-6=”Genetics account for roughly 25–40% of cases.” image-6=”” headline-7=”h3″ question-7=”Do baby teeth problems always lead to permanent buck teeth?” answer-7=”Not always, but untreated issues can increase the risk.” image-7=”” headline-8=”h3″ question-8=”How can parents tell if their child is at risk for buck teeth?” answer-8=”Watch for habits like thumb sucking, mouth breathing, or jaw misalignment.” image-8=”” headline-9=”h3″ question-9=”What should parents do if they notice early signs of buck teeth?” answer-9=”Consult a pediatric dentist or orthodontist promptly.” image-9=”” headline-10=”h3″ question-10=”Are there any exercises that can prevent buck teeth formation?” answer-10=”Yes, orofacial myofunctional therapy may help in some cases.” image-10=”” headline-11=”h3″ question-11=”How do buck teeth affect speech development in children?” answer-11=”They can cause lisps or difficulty with certain sounds.” image-11=”” headline-12=”h3″ question-12=”Can buck teeth cause other dental problems later in life?” answer-12=”Yes, they can lead to jaw pain, wear on teeth, and bite issues.” image-12=”” headline-13=”h3″ question-13=”What age is too late to correct the causes of buck teeth?” answer-13=”It’s never too late, but early treatment (before age 12) is often most effective.” image-13=”” headline-14=”h3″ question-14=”Do certain ethnicities have higher rates of buck teeth?” answer-14=”Some studies suggest slight differences, but overall rates are similar globally.” image-14=”” headline-15=”h3″ question-15=”How do buck teeth causes differ between upper and lower protrusion?” answer-15=”Upper protrusion is often caused by habits; lower by jaw structure or genetics.” image-15=”” headline-16=”h3″ question-16=”Can nutritional deficiencies during pregnancy cause buck teeth?” answer-16=”Not directly, but poor nutrition can affect fetal jaw and tooth development.” image-16=”” headline-17=”h3″ question-17=”What role do baby teeth play in permanent buck teeth formation?” answer-17=”They guide permanent teeth; early loss or misalignment can lead to problems.” image-17=”” headline-18=”h3″ question-18=”How do modern parenting practices contribute to buck teeth rates?” answer-18=”Increased pacifier use, bottle-feeding, and screen time may raise the risk.” image-18=”” headline-19=”h3″ question-19=”What environmental toxins might contribute to buck teeth development?” answer-19=”Exposure to lead, BPA, and other endocrine disruptors may affect jaw growth.” image-19=”” count=”20″ html=”true” css_class=””]