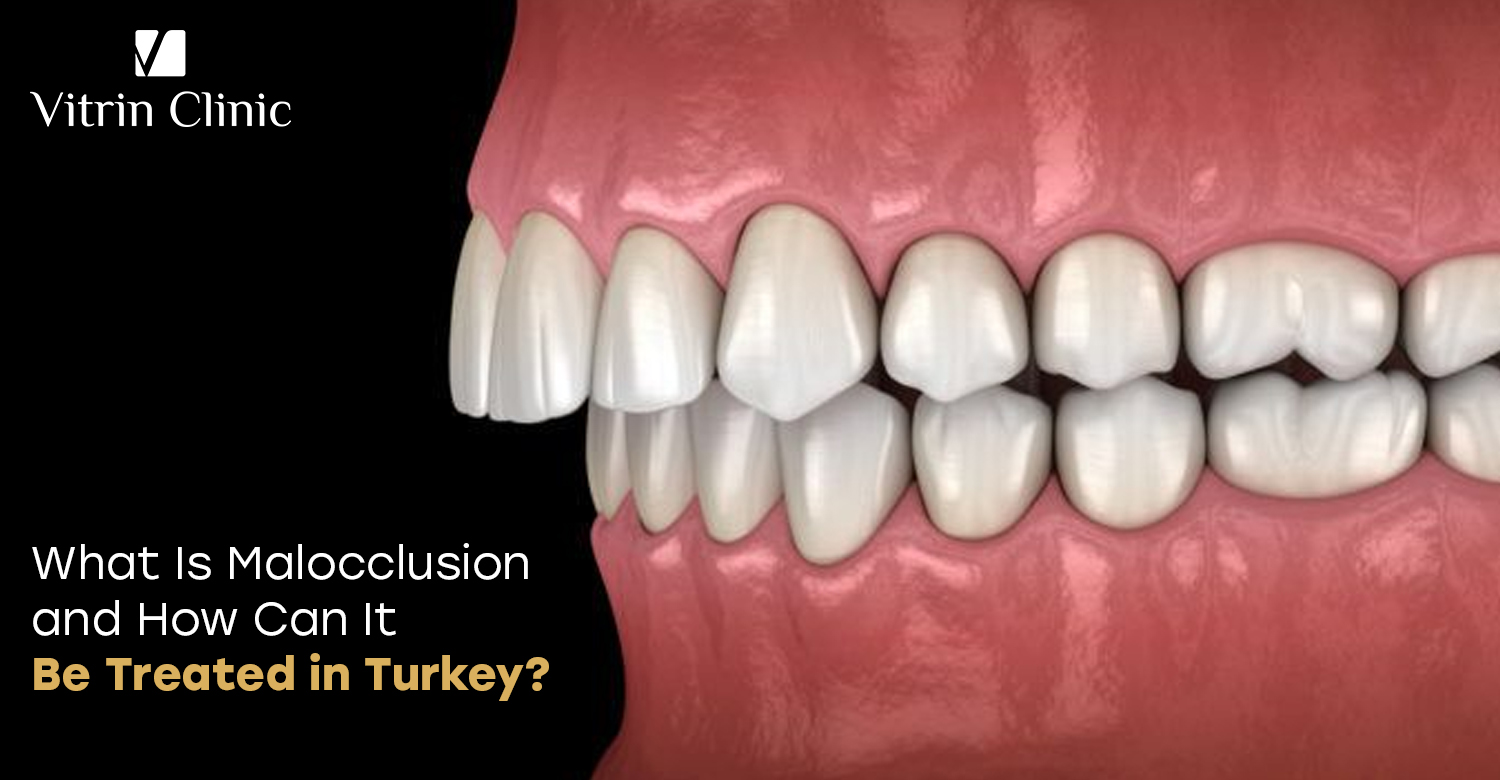
What Is Malocclusion and Why Does It Matter for Oral Health?
Malocclusion is a dental condition where the teeth and jaws do not align properly when the mouth is closed. This misalignment affects oral health by causing problems with chewing, speaking, oral hygiene, and jaw function. If left untreated, malocclusion can lead to tooth wear, gum disease, and jaw pain. It also impacts aesthetics, affecting your smile and confidence.
What Are the Main Causes of Malocclusion?
Malocclusion can be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genetics can determine jaw size, shape, and tooth size, while habits like thumb-sucking or tongue thrusting, missing or extra teeth, and jaw size differences also play a role.
Is malocclusion genetic or inherited?
Yes, malocclusion is often inherited from parents because genes influence jaw and tooth development.
Which genes are linked to jaw and teeth alignment?
Genes such as MSX1 and PAX9 are linked to jaw bone growth and tooth formation, affecting how teeth align.
Can malocclusion skip generations?
Yes, genetic traits for malocclusion can skip generations, meaning a child may inherit misalignment even if parents don’t show it.
Can thumb-sucking cause malocclusion?
Yes, prolonged thumb-sucking can exert pressure on the teeth and jaws, causing misalignment.
At what age does thumb-sucking become harmful?
Thumb-sucking becomes harmful if it continues beyond age 3-4 when permanent teeth start erupting.
What types of malocclusion are caused by prolonged thumb-sucking?
It often causes anterior open bite and protruding upper front teeth (overjet).
How does jaw size affect malocclusion?
Jaw size impacts how teeth fit in the mouth. A mismatch between upper and lower jaw size can cause malocclusion.
Can a small jaw cause overcrowding?
Yes, a small jaw may not have enough space, leading to crowding of teeth.
Why does a large jaw lead to spacing problems?
A large jaw may create extra space, causing gaps between teeth.
Do missing or extra teeth lead to malocclusion?
Yes, missing teeth cause neighboring teeth to shift; extra teeth can crowd or push teeth out of alignment.
How do wisdom teeth contribute to malocclusion?
Impacted wisdom teeth can push adjacent molars forward, causing crowding.
Can supernumerary teeth push other teeth out of alignment?
Yes, extra teeth occupy space needed for normal teeth, causing misalignment.
How do habits like tongue thrusting contribute to malocclusion?
Tongue thrusting puts pressure on teeth, pushing them forward and affecting bite development.
How does tongue position affect bite development?
An improper tongue position can prevent proper closure of teeth, causing open bite or other misalignments.
What Are the Different Types of Malocclusion?
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Class I | Normal bite, but teeth are misaligned or crowded |
| Class II | Overbite – upper jaw/teeth protrude |
| Class III | Underbite – lower jaw/teeth protrude |
| Crossbite | Upper teeth sit inside lower teeth |
| Open Bite | Front teeth don’t touch when biting |
| Deep Bite | Upper front teeth cover lower teeth too much |
| Crowding | Not enough space for proper alignment |
| Spacing | Gaps between teeth |
| Impacted Teeth | Teeth stuck in bone or gum |
What is Class I malocclusion?
Class I malocclusion is when the bite is normal but there is crowding, spacing, or misaligned teeth.
What is Class II malocclusion (overbite)?
Class II malocclusion occurs when the upper teeth significantly overlap the lower teeth.
What are the subtypes of Class II malocclusion?
- Division 1: Upper front teeth protrude outward.
- Division 2: Upper front teeth tilt backward.
What is Class III malocclusion (underbite)?
Class III is when the lower teeth protrude beyond the upper teeth, causing an underbite.
Why is Class III malocclusion more complex to treat?
Because it often involves jaw bone discrepancies requiring surgery in addition to orthodontics.
What is an open bite and why does it happen?
An open bite is when front or back teeth do not touch when biting down. It happens due to habits or jaw growth problems.
What are the differences between anterior and posterior open bite?
Anterior open bite involves front teeth not touching; posterior open bite involves back teeth not touching.
What is a crossbite?
A crossbite occurs when the upper teeth sit inside the lower teeth instead of outside. It can affect one tooth, several teeth, or an entire side of the mouth. Crossbites may lead to uneven wear, gum problems, and jaw discomfort if left untreated.
What is the difference between unilateral and bilateral crossbite?
A unilateral crossbite affects teeth on only one side of the mouth, while a bilateral crossbite impacts both sides. Unilateral cases often cause asymmetrical jaw growth, while bilateral crossbites may affect overall bite function and alignment more extensively.
What is a deep bite?
A deep bite occurs when the upper front teeth excessively overlap the lower front teeth vertically. This condition can cause gum irritation, tooth wear, and even jaw strain. Severe deep bites may also affect appearance and lead to functional problems when chewing.
What is crowding and spacing in malocclusion?
Crowding happens when there isn’t enough space in the jaw, causing teeth to overlap or twist. Spacing is the opposite, where excessive gaps exist between teeth. Both issues are types of malocclusion that can affect chewing, aesthetics, and overall dental health.
What Are the Common Symptoms of Malocclusion?
Common symptoms include crooked or crowded teeth, difficulty chewing, speech issues, frequent biting of cheeks, jaw pain, and headaches. Some patients also notice uneven tooth wear and dissatisfaction with their smile. Symptoms vary depending on severity and type of malocclusion.
How does malocclusion affect chewing?
Malocclusion can make chewing inefficient by misaligning the teeth, preventing them from meeting properly. This leads to uneven pressure, incomplete food breakdown, and digestive strain. Severe cases may also cause discomfort or jaw fatigue when eating harder foods.
Can malocclusion cause difficulty biting into food?
Yes. When teeth are misaligned, the front teeth may not meet properly, making it hard to bite into foods like apples or sandwiches. Overbites, underbites, or open bites often cause this issue, affecting both function and comfort while eating.
Can malocclusion cause speech problems?
Yes. Misaligned teeth can interfere with tongue placement and airflow during speech. This may cause lisping, unclear pronunciation, or difficulty with certain sounds. Severe malocclusion can make communication challenging and may impact confidence in speaking situations.
What speech sounds are affected by malocclusion?
Sounds requiring precise tongue and teeth coordination are most affected, especially “s,” “z,” “t,” “d,” and “th.” Malocclusion may cause lisping or distortion, as the tongue cannot properly contact teeth or palate, leading to unclear or altered speech production.
Why does malocclusion lead to jaw pain or headaches?
Misaligned teeth strain the jaw muscles and temporomandibular joint (TMJ). Over time, this imbalance causes tension, leading to jaw pain, clicking sounds, and headaches. Chronic clenching or uneven chewing pressure further worsens discomfort in patients with malocclusion.
Can malocclusion cause aesthetic concerns?
Yes. Malocclusion often results in crooked, protruding, or uneven teeth, affecting smile appearance. It can also change facial balance, making the jawline look asymmetrical. Many patients seek treatment not only for function but also for improved aesthetics and confidence.
How does malocclusion affect smile symmetry?
Uneven or crooked teeth create an unbalanced smile.
How does malocclusion affect oral hygiene?
Crowded or crooked teeth trap food and plaque, making cleaning difficult.
Why is tooth crowding harder to clean?
Overlapping teeth create hard-to-reach areas where plaque accumulates.
How Is Malocclusion Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves clinical exams, imaging, and sometimes specialized analysis.
What role do dental exams play in diagnosis?
Dentists assess bite, alignment, and jaw movement during exams.
How are X-rays used in malocclusion assessment?
X-rays reveal bone structure, tooth position, and impacted teeth.
What is cephalometric analysis?
A specialized X-ray measuring jaw relationships and growth patterns.
What does cephalometric analysis reveal about jaw growth?
It shows jaw size, angle, and growth trends critical for planning treatment.
Can digital scans help in identifying malocclusion?
Yes, digital 3D scans provide precise images of teeth and jaws.
How accurate are 3D digital scans compared to traditional impressions?
3D scans are more accurate, faster, and less uncomfortable than traditional molds.
What Are the Best Treatments for Malocclusion?
Treatment depends on severity and type but mainly involves orthodontics and sometimes surgery.
How do braces correct malocclusion?
Braces apply continuous pressure to shift teeth gradually into correct position.
What types of braces are available today?
Metal, ceramic, lingual, and clear aligners.
How do metal braces compare to ceramic braces?
Metal braces are more durable; ceramic braces are less visible but more fragile.
What role do clear aligners (Invisalign) play?
Aligners straighten teeth discreetly and are removable.
Are aligners effective for severe malocclusion cases?
They work best for mild to moderate cases; severe cases may need braces or surgery.
Can retainers help fix malocclusion?
Retainers mainly keep teeth in place after treatment; some mild corrections are possible.
When is orthodontic surgery required for malocclusion?
Surgery is needed when jaw bone discrepancies cause severe bite problems.
How long does malocclusion treatment usually take?
Treatment ranges from 6 months to 3 years based on complexity.
What Are the Surgical Options for Severe Malocclusion?
| Surgical Procedure | Purpose | Used For | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maxillary Osteotomy | Repositions the upper jaw (maxilla) | Overbite, open bite, crossbite, midface deficiency | Often improves facial symmetry and nasal airflow |
| Mandibular Osteotomy | Repositions the lower jaw (mandible) | Underbite, receding chin/lower jaw | Can cause temporary numbness in the lower lip and chin |
| Bimaxillary Osteotomy | Adjusts both upper and lower jaws simultaneously | Complex Class III malocclusion, severe asymmetry | Most comprehensive; longer recovery time |
| Genioplasty | Reshapes or repositions the chin | Chin deficiency or excess; facial balance | Often combined with other jaw surgeries |
| SARPE (Surgically Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion) | Widens the upper jaw | Crossbite, severe crowding, narrow upper arch | Used when the growth plates have fused (mainly in adults) |
| Distraction Osteogenesis | Gradually lengthens jawbone using a mechanical device | Severe jaw underdevelopment, congenital defects | Slower process but avoids bone grafts |
| Surgical Tooth Extraction | Removes impacted or overcrowded teeth | Preparation for orthodontic treatment or to relieve crowding | Often done before braces or jaw surgery |
What is orthognathic surgery?
Orthognathic surgery corrects jaw irregularities to improve bite and facial appearance.
How is orthognathic surgery performed step by step?
- Pre-surgical orthodontics and planning
- Surgical repositioning of jaw bones
- Fixation with plates/screws
- Post-surgical orthodontics and healing
How does jaw surgery correct malocclusion?
By repositioning jaws for proper alignment and bite.
When is tooth extraction needed in malocclusion treatment?
Extraction creates space for crowded teeth to align properly.
How Does Malocclusion Affect Children and Adults Differently?
| Aspect | Children | Adults |
|---|---|---|
| Jaw Growth Potential | Jawbones are still growing, allowing easier correction with orthodontics | Growth is complete, limiting non-surgical options |
| Early Intervention Benefits | Orthodontic appliances can guide jaw development | Missed early treatment may require surgery in severe cases |
| Tooth Eruption Issues | Malocclusion may cause or result from delayed/misaligned tooth eruption | May have impacted, worn, or missing teeth from long-term issues |
| Treatment Options | Often involves interceptive orthodontics (e.g., expanders, headgear) | Requires full braces, aligners, or surgical correction |
| Compliance with Treatment | May need more parental involvement and motivation | Adults are typically more consistent, but may have time/work constraints |
| Psychosocial Impact | Can lead to bullying, speech issues, or self-esteem problems | Affects confidence, professional interactions, or social anxiety |
| Functional Problems | May cause issues with chewing, speech, or facial development | Can cause jaw pain (TMJ), headaches, tooth wear, or gum disease |
| Habits That Influence It | Thumb sucking, pacifier use, tongue thrusting | Bruxism (teeth grinding), tooth loss, or poorly fitting dental work |
| Treatment Time & Cost | Often shorter and less costly if treated early | Longer and more expensive; insurance may not always cover adult care |
How common is malocclusion in children?
Very common; early detection is important for best outcomes.
When is the best age to treat malocclusion?
Treatment often begins around age 7 when permanent teeth start to erupt.
What are the benefits of early orthodontic intervention?
It guides jaw growth, prevents worsening, and shortens later treatment.
Can malocclusion develop in adults?
Yes, malocclusion can develop or worsen in adulthood.
What are the risks of untreated malocclusion in adults?
Risks include tooth wear, gum disease, TMJ disorders, and aesthetic issues.
What Are the Health Risks of Untreated Malocclusion?
Increased risk of tooth decay and gum disease due to poor oral hygiene.
Jaw pain and TMJ disorders from uneven bite pressure.
Chewing and speech difficulties affecting nutrition and communication.
Excessive tooth wear, cracking, or even tooth loss over time.
Negative impact on self-esteem and mental well-being.
Can malocclusion cause tooth decay and gum disease?
Yes, because crowded teeth trap plaque harder to remove.
How does malocclusion affect digestion?
Poor chewing leads to inadequate food breakdown, impacting digestion.
Can malocclusion lead to temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ)?
Yes, malocclusion stresses the TMJ causing pain and dysfunction.
What are the early signs of TMJ caused by malocclusion?
Jaw pain, clicking sounds, headaches, and difficulty opening mouth.
How does malocclusion impact facial aesthetics and confidence?
It can cause facial asymmetry and reduced self-esteem due to an unattractive smile.
How Can Malocclusion Be Prevented or Controlled?
- Early dental checkups
Regular visits help detect and manage jaw or tooth alignment issues early. - Address oral habits early
Stop thumb sucking, pacifier use (past age 2–3), tongue thrusting, or nail biting. - Proper oral hygiene
Prevents premature tooth loss from decay, which can lead to shifting teeth. - Timely orthodontic evaluation
Children should be assessed by age 7 to catch issues while the jaw is still growing. - Use of space maintainers or expanders
These devices guide proper jaw growth and tooth eruption when baby teeth are lost early. - Manage injury risks
Wear mouth guards during sports to prevent trauma that could misalign the jaw. - Avoid prolonged bottle feeding
Prolonged bottle use or poor feeding posture can affect bite development. - Treat dental issues promptly
Untreated cavities or infections can lead to tooth loss and misalignment.
Can early orthodontic intervention prevent malocclusion?
Yes, early treatment guides jaw development and reduces severity.
How can parents help prevent malocclusion in children?
By monitoring habits and ensuring regular dental check-ups.
Which childhood habits should parents monitor?
Thumb-sucking, prolonged pacifier use, tongue thrusting, and mouth breathing.
Does breaking oral habits reduce malocclusion risk?
Yes, stopping harmful habits allows normal jaw and teeth development.
Can regular dental check-ups control malocclusion development?
Early detection during check-ups allows timely intervention.
How Do Turkish Clinics Treat Malocclusion?
| Treatment Type | Description & Use |
|---|---|
| Traditional Metal Braces | Standard, effective treatment using metal brackets and wires. Powerful and cost-effective. |
| Ceramic (Clear) Braces | Tooth-colored or translucent braces offer a more subtle appearance. Comparable efficacy to metal braces. |
| Lingual Braces | Brackets placed on the interior surfaces of teeth are completely hidden. Ideal for aesthetics, though trickier to clean. |
| Self-Ligating Braces (e.g., Damon) | Use sliding mechanisms to reduce friction and potentially shorten treatment times. |
| Clear Aligners (e.g., Invisalign, ClearCorrect) | Removable, nearly invisible trays that are especially popular among teens and adults. Comfortable, low maintenance. |
| Palatal Expanders & Functional Appliances | Used mainly in growing children to widen the upper jaw or modify jaw positioning (e.g., twin-block appliances). |
| Orthognathic (Jaw) Surgery | For severe skeletal malocclusion collaboration between orthodontists and oral surgeons to realign jaws. |
What orthodontic treatments are available in Turkey?
Braces, clear aligners, orthodontic surgery, and digital treatment planning.
How affordable is malocclusion treatment in Turkey compared to Europe?
Treatment in Turkey is generally 40-70% cheaper while maintaining high quality.
Why do international patients choose Turkey for orthodontic care?
Lower cost, experienced doctors, advanced technology, and comprehensive care.
What advanced technologies do Turkish clinics use for malocclusion?
3D digital imaging, CAD/CAM technology, laser treatments, and computer-guided surgery.
Do Turkish clinics use 3D imaging for treatment planning?
Yes, 3D imaging is widely used for precise diagnosis and personalized treatment.
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h3″ question-0=”What are the early signs of malocclusion?” answer-0=”Difficulty biting, speech problems, crooked teeth, and jaw discomfort.” image-0=”” headline-1=”h3″ question-1=”Can malocclusion fix itself without treatment?” answer-1=”No, malocclusion usually worsens without treatment.” image-1=”” headline-2=”h3″ question-2=”How long do braces take to correct malocclusion?” answer-2=”Typically 1 to 3 years.” image-2=”” headline-3=”h3″ question-3=”Are clear aligners effective for severe malocclusion?” answer-3=”They are best for mild to moderate cases; severe malocclusion may require braces or surgery.” image-3=”” headline-4=”h3″ question-4=”Can malocclusion return after treatment?” answer-4=”Yes, if retainers are not worn as directed.” image-4=”” headline-5=”h3″ question-5=”Is malocclusion treatment painful?” answer-5=” Some discomfort is normal, especially after adjustments, but pain is manageable.” image-5=”” headline-6=”h3″ question-6=”What is the recovery time after jaw surgery for malocclusion?” answer-6=”Typically 6 to” image-6=”” count=”7″ html=”true” css_class=””]