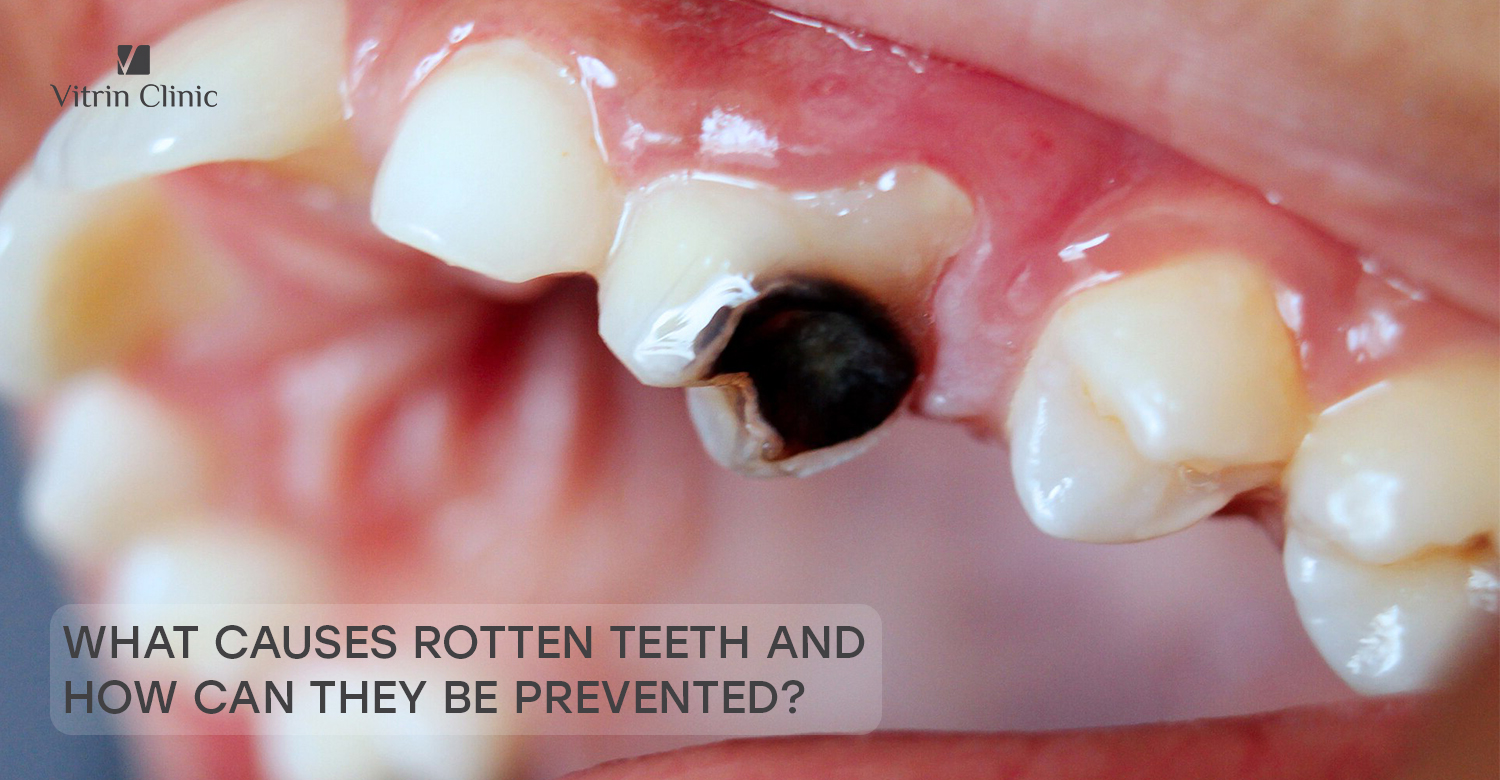
Rotten teeth are teeth that have suffered decay or significant damage primarily caused by bacterial infection and poor oral care. This decay results from the gradual breakdown of the hard outer layer of the tooth, called enamel, and the softer inner layer known as dentin. When these protective layers deteriorate, cavities form, leading to structural weakening of the tooth.
How Can I Identify Rotten Teeth Early?
Early detection of rotten teeth is crucial to prevent progression and complicated treatment. Initially, rotten teeth may show subtle changes such as white spots or chalky areas on the tooth surface, indicating enamel demineralization. As decay progresses, you may see brownish or dark stains where bacteria have compromised the tooth structure.
What Causes Teeth to Rot?
The primary cause of teeth rotting is the buildup of dental plaque, a sticky, colorless film that continuously forms on teeth. This plaque is loaded with bacteria that thrive on sugars and carbohydrates from food and drinks. When bacteria metabolize these sugars, they produce acids that slowly erode the protective enamel layer through a process called demineralization. Without proper oral hygiene, plaque hardens into tartar, making it harder to clean and accelerating damage.
Are Rotten Teeth Dangerous for My Overall Health?
Yes, the consequences of rotten teeth extend far beyond oral discomfort or aesthetics. Untreated tooth decay can lead to serious local complications such as dental abscesses, painful pus-filled infections, gum disease, and eventual tooth loss.
These oral infections can serve as reservoirs of bacteria entering the bloodstream, potentially triggering systemic inflammation and worsening chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes. Research has linked poor oral health with higher risks of stroke, respiratory infections, and adverse pregnancy outcomes such as premature birth.
How Does Poor Oral Hygiene Lead to Rotten Teeth?
Poor oral hygiene creates the perfect environment for plaque accumulation. Without regular and thorough brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, which is difficult to remove and continues to harbor harmful bacteria.
The enamel breaks down, allowing cavities to form, which worsen over time and cause the teeth to rot. Inadequate hygiene also increases the likelihood of gum disease, further compromising oral health.
How Does Poor Oral Hygiene Lead to Rotten Teeth?
Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque buildup, which harbors decay-causing bacteria. Over time, these bacteria produce acids that attack the enamel, creating cavities and rotten teeth.
Can Diet Affect Tooth Decay?
Absolutely. Frequent consumption of sugary, acidic foods and beverages fuels bacterial growth and acid production, accelerating tooth decay. A diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports enamel strength and overall dental health.
Do Genetics Play a Role in Tooth Decay?
Yes, genetics can influence enamel strength, saliva composition, and susceptibility to bacteria, making some individuals more prone to rotten teeth than others.
How Do Bacteria Contribute to Tooth Rot?
Bacteria in plaque metabolize carbohydrates from food, producing acids that dissolve enamel. Over time, this creates cavities and deeper decay known as rotten teeth.
Can Certain Medical Conditions Cause Rotten Teeth?
Conditions such as dry mouth (xerostomia), diabetes, and acid reflux increase the risk of tooth decay by altering the mouth’s environment, reducing saliva, or increasing acid exposure. Root canal therapy removes infection and preserves your natural tooth structure. Know more about save the tooth.
What Are the Symptoms of Rotten Teeth?
Rotten teeth often manifest through a combination of physical signs and sensations. Key symptoms include tooth discoloration, visible holes or pits on the surface, tooth sensitivity particularly to hot or cold temperatures, persistent toothache, bad breath, and sometimes swelling or tenderness in the surrounding gums. As decay progresses, discomfort may increase, and chewing can become painful or difficult.
How Do Rotten Teeth Feel?
Rotten teeth typically cause a range of unpleasant sensations. Many people experience sharp or aching pain that can be intermittent or constant, especially when eating or drinking hot, cold, or sugary foods. This sensitivity results from the breakdown of enamel and exposure of the dentin or nerve endings inside the tooth.
Can Rotten Teeth Cause Bad Breath?
Yes, rotten teeth are a common cause of bad breath (halitosis). The decayed tooth tissue and bacterial overgrowth produce foul-smelling sulfur compounds and toxins. These odors persist despite regular brushing and become worse if decay or infection is left untreated.
Know more about rotten tooth extraction.
Are Rotten Teeth Visible to the Naked Eye?
Often, rotten teeth show clear visual signs. Early decay may appear as white spots indicating enamel loss, while more advanced cavities present as brown, black, or darkened stains on the tooth surface. Severe decay can cause noticeable holes, pits, or fractures in the tooth. Teeth may also look irregular, broken down, or stained, making rotten teeth visible to anyone looking closely.
Can Rotten Teeth Cause Pain or Sensitivity?
Yes, pain and sensitivity are hallmark symptoms of rotten teeth. When decay reaches the deeper layers of the tooth, it irritates the nerves, causing sharp sensitivity or persistent toothache. Sensitivity usually occurs in response to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. If untreated, this pain can worsen and lead to abscess formation or infection, requiring urgent dental treatment.
How Can Rotten Teeth Be Treated?
Rotten teeth treatment depends on the stage and severity of decay. Early detection allows for less invasive solutions, while advanced decay requires more complex dental procedures to restore tooth health, function, and aesthetics.
When Should I See a Dentist for Rotten Teeth?
You should see a dentist promptly if you notice any signs of rotten teeth such as persistent sensitivity, visible cavities or dark spots, tooth pain, or swelling. Early evaluation prevents complications like infections, abscesses, and tooth loss by enabling timely intervention.
What Dental Procedures Can Fix Rotten Teeth?
- Fillings: Used to remove decayed material and fill cavities in early to moderate decay.
- Crowns: Caps placed over damaged teeth to restore shape, strength, and appearance when decay is extensive.
- Root canal therapy: Required if decay reaches the tooth pulp, removing infection and preserving the tooth.
- Tooth extraction: Performed when the tooth is too damaged to be saved or infected beyond repair.
These treatments effectively restore function and prevent further damage. Brush with fluoride, floss daily, and limit sugar to stop decay before it starts. Know more about preventing rotten teeth.
Can Rotten Teeth Be Reversed Without Surgery?
In very early stages, enamel demineralization or superficial cavities can sometimes be reversed or arrested using professional fluoride treatments, dental sealants, and improved oral hygiene. However, once decay forms cavities or affects deeper layers, surgery or fillings become necessary.
Are There Home Remedies for Rotten Teeth?
Home care practices such as thorough brushing with fluoride toothpaste, daily flossing, and using antimicrobial mouth rinses support oral health and help prevent further decay.
How Effective Are Fillings and Crowns for Rotten Teeth?
Fillings are highly effective for repairing small to medium-sized cavities by sealing and protecting the tooth. Crowns offer stronger, longer-lasting protection for extensively decayed or structurally compromised teeth, restoring chewing function and preventing fractures. Know more about preventing rotten teeth.
When Is Tooth Extraction Necessary?
Tooth extraction is necessary when rotten teeth are severely decayed, cracked, or infected beyond the point of repair. Extraction is also considered if the tooth threatens surrounding teeth, causes persistent pain, or is linked to abscess formation. After extraction, options like dental implants or bridges restore function and appearance.
How Can Rotten Teeth Be Prevented?
Preventing rotten teeth involves consistent oral hygiene, a healthy diet, and regular dental care. Adopting daily habits that limit bacterial growth and enamel erosion is key to maintaining strong, decay-free teeth.
What Daily Habits Protect Against Tooth Decay?
- Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste removes plaque and food debris that feed decay-causing bacteria.
- Flossing daily clears plaque and particles between teeth where brushes can’t reach.
- Limiting sugar intake, especially sugary snacks and drinks, reduces acid production by bacteria.
- Drinking plenty of water helps wash away food residues and maintains saliva flow, which naturally protects teeth.
Know more about dental implants.
How Important Is Brushing and Flossing?
Brushing and flossing are essential for preventing rotten teeth because they physically remove the sticky plaque and bacteria that produce enamel-eroding acids. Without these daily habits, plaque hardens into tartar, making decay much more difficult to control and increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Can Mouthwash Prevent Rotten Teeth?
Antibacterial and fluoride mouthwashes can be effective adjuncts in preventing rotten teeth. They reduce bacterial levels and can help strengthen enamel, especially in individuals prone to decay. However, mouthwash should never replace brushing and flossing but rather complement them as part of a comprehensive oral hygiene routine.
How Does Diet Influence Dental Health?
Diet heavily influences tooth decay risk. Frequent consumption of sugary and acidic foods encourages bacterial acid production and enamel erosion. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals like calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus supports enamel repair and overall oral health, reducing the chances of rotten teeth.
How Often Should I Visit the Dentist to Avoid Rotten Teeth?
Routine dental check-ups every six months are recommended. These visits allow early detection of decay and plaque buildup, professional cleanings, and timely treatments to prevent minor problems from turning into rotten teeth and other oral health issues.
Can Fluoride Treatments Help Prevent Tooth Decay?
Yes, fluoride treatments provided by dentists strengthen tooth enamel by enhancing remineralization and inhibiting bacterial acid effects.
They can help reverse very early decay stages, making fluoride a powerful preventive measure against rotten teeth, especially for individuals at higher risk. When a tooth is too decayed to save, removal stops infection and relieves pain. Know more about extraction.
What Are the Risks of Untreated Rotten Teeth?
Untreated rotten teeth carry significant risks that affect both oral and overall health. The decay can advance deeper into the tooth, causing severe pain, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues.
It may lead to complications such as abscesses, tooth loss, and difficulty eating or speaking.
Can Rotten Teeth Cause Gum Disease?
Yes, rotten teeth can directly contribute to gum disease. As decay progresses, bacteria spread from the tooth to the surrounding gum tissue, causing inflammation known as gingivitis.
If untreated, this can advance to periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease characterized by gum recession, bone loss, and potential tooth mobility or loss.
Can Tooth Decay Lead to Infections?
Absolutely. When decay reaches the inner pulp of a tooth, it can cause infection, sometimes forming an abscess, a painful, pus-filled swelling. Abscesses can spread bacteria locally and, in severe cases, enter the bloodstream, leading to systemic infections that require urgent medical care.
Can Rotten Teeth Affect My Overall Health?
Yes, the effects of untreated rotten teeth extend beyond the mouth. Chronic oral infections increase systemic inflammation, which is linked to higher risks of heart disease, stroke, diabetes complications, respiratory infections, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Managing rotten teeth is therefore essential not only for oral health but also to reduce risks of serious systemic illnesses.
Can Untreated Rotten Teeth Affect My Appearance?
Yes, rotten teeth can significantly impact your appearance. Decay causes dark spots, holes, and discoloration. Severe decay may result in broken or missing teeth, altering your smile and facial structure.
Over time, bone loss from untreated decay can cause facial sagging and a prematurely aged look, affecting confidence and social interactions. Plaque bacteria feed on sugar and produce acid that erodes enamel. Know more about causes of tooth decay.
Are Rotten Teeth Common in Turkey?
Yes, rotten teeth and dental decay remain common issues in Turkey. Studies show a high prevalence of dental caries across all age groups, reflecting widespread challenges in oral health despite ongoing preventive efforts.
What Are the Statistics of Dental Decay in Turkey?
According to recent national data, the prevalence of dental caries among the Turkish population is around 76.5%, indicating that over three-quarters of people experience tooth decay at some point. Among children, the pooled prevalence is approximately 75.6%, signaling a significant public health concern.
Are There Regional Differences in Tooth Decay Rates?
Yes, there are notable regional disparities. Urban residents tend to have better access to dental care and preventive services, resulting in lower caries rates compared to rural areas where access is limited.
Sociodemographic factors like education level and income also influence these variations, with rural populations and less-educated groups often experiencing higher decay rates.
How Does Access to Dental Care Affect Rotten Teeth in Turkey?
Limited access to affordable and regular dental care contributes significantly to the prevalence and severity of rotten teeth in Turkey. The annual dental visit frequency in Turkey is around 0.4%, substantially lower than the 5% average in European countries.
Know more about endodontic microsurgery.
What Are the Costs of Treating Rotten Teeth in Turkey?
The cost of treating rotten teeth in Turkey varies depending on the type and complexity of the dental procedure. Turkey is renowned for offering high-quality dental care at affordable prices, making it a popular destination for those seeking cost-effective treatments for tooth decay and related problems.
How Much Does a Filling Cost in Turkey?
Dental fillings in Turkey typically range from $40 to $100 for standard materials like amalgam or composite resin. More advanced or aesthetic options such as ceramic or gold fillings can cost between $150 and $500 depending on the clinic and material used. These prices include the examination, decay removal, and filling placement, making fillings an accessible option for repairing cavities in early to moderate stages.
How Much Does Tooth Extraction Cost?
Tooth extractions in Turkey are generally affordable, ranging from about $45 to $150. The price depends on the complexity of the extraction and whether it is a simple or surgical procedure. Extractions are often performed when teeth are severely decayed or damaged beyond repair.
Know more about symptoms of a rotten tooth.
How Expensive Are Crowns and Implants?
Crowns and dental implants are more costly but provide durable, long-term solutions for rotten and missing teeth. Zirconium or ceramic crowns typically range from $100 to $300 per tooth, while dental implants, including the abutment and crown, cost between $400 and $1,000 for a single implant. Full-mouth implant restorations such as all-on-4 or all-on-6 implant systems can range from $3,000 to $7,000 depending on the clinic and package.
Are There Affordable Dental Clinics in Turkey?
Yes, Turkey hosts many dental clinics that combine competitive pricing with modern technology and skilled dentists.
Clinics in major cities like Istanbul, Izmir, and Antalya offer high-quality treatments with packages that may include accommodation and transportation, making rotten teeth treatment accessible and convenient for both locals and international patients.
Turkey provides exceptional value for dental care, making it a favored destination for those seeking effective treatment for rotten teeth without compromising on quality or safety. Rotten teeth not only damage your smile but also put your health at risk. Look for white spots, dark stains, sensitivity, and persistent bad breath. Know more about rotten tooth symptoms.
If you’re seeking reliable and affordable rotten teeth treatment in Turkey, visit vitrinclinic.com for expert care and personalized solutions. Take advantage of their Free Consultation to discuss your dental needs with experienced professionals and start your journey to a healthier smile today.
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h3″ question-0=”Can Rotten Teeth Heal on Their Own?” answer-0=”No, professional treatment is necessary to fix rotten teeth once decay has progressed.” image-0=”” headline-1=”h3″ question-1=”How Long Does It Take for Teeth to Rot Completely?” answer-1=”Decay progression varies but can worsen over months to years without intervention.” image-1=”” headline-2=”h3″ question-2=”Can Children Have Rotten Teeth?” answer-2=”Yes, children are susceptible to cavities and rotten teeth, especially with poor oral hygiene.” image-2=”” headline-3=”h3″ question-3=”Are Rotten Teeth Contagious?” answer-3=”Tooth decay bacteria can be transmitted, but rotten teeth themselves are not contagious.” image-3=”” headline-4=”h3″ question-4=”Does Sugar Cause Rotten Teeth?” answer-4=”Sugar fuels the bacteria that cause decay, increasing rotten teeth risk.” image-4=”” headline-5=”h3″ question-5=”Can Smoking Cause Rotten Teeth?” answer-5=”Smoking contributes to decay and gum disease, worsening rotten teeth.” image-5=”” headline-6=”h3″ question-6=”Is It Safe to Ignore a Rotten Tooth?” answer-6=”Ignoring rotten teeth can lead to infection, pain, and tooth loss.” image-6=”” headline-7=”h3″ question-7=”Can Rotten Teeth Affect My Heart or Other Organs?” answer-7=”Yes, untreated dental infections have been linked to heart problems and systemic inflammation.” image-7=”” headline-8=”h3″ question-8=”How Can I Tell the Difference Between a Cavity and Rotten Tooth?” answer-8=”A cavity is an early sign of decay; rotten teeth indicate advanced damage.” image-8=”” headline-9=”h3″ question-9=”What Is the Best Way to Stop Tooth Decay Before It Becomes Rotten Teeth?” answer-9=”Maintain good oral hygiene, regular dental visits, and limit sugar intake to prevent tooth decay.” image-9=”” count=”10″ html=”true” css_class=””]